Adjusted trial balance example and explanation
But outside of the accountingdepartment, why is the adjusted trial balance important to the restof the organization? An employee or customer may not immediatelysee the impact of the adjusted trial balance on his or herinvolvement with the company. A company’s transactions are recorded in a general ledger and later summed to be included in a trial balance. Ending retained earnings information is taken from the statement of retained earnings, and asset, liability, and common stock information is taken from the adjusted trial balance as follows.
Ten-Column Worksheets
Liquidity refers to how easily an item can be converted to cash. IFRS requires that accounts be classified into current and noncurrent categories for both assets and liabilities, but no specific presentation format is required. Thus, for US companies, the first category always seen on a Balance Sheet is Current Assets, and the first account balance reported is cash. The accounts of a Balance Sheet using IFRS might appear as shown here. For example, IFRS-based financial statements are only required to report the current period of information and the information for the prior period. US GAAP has no requirement for reporting prior periods, but the SEC requires that companies present one prior period for the Balance Sheet and three prior periods for the Income Statement.
Trial Balance: Definition, How It Works, Purpose, and Requirements
- A trial balance simply shows a list of the ledger accounts and their balances.
- Both the debit and credit columns are calculated at the bottom of a trial balance.
- It acts as an auditing tool, while a balance sheet is a formal financial statement.
- Since most companies have computerized accounting systems, they rarely manually create a TB or have to check for out-of-balance errors.
- There are five sets of columns, each set having a column for debit and credit, for a total of 10 columns.
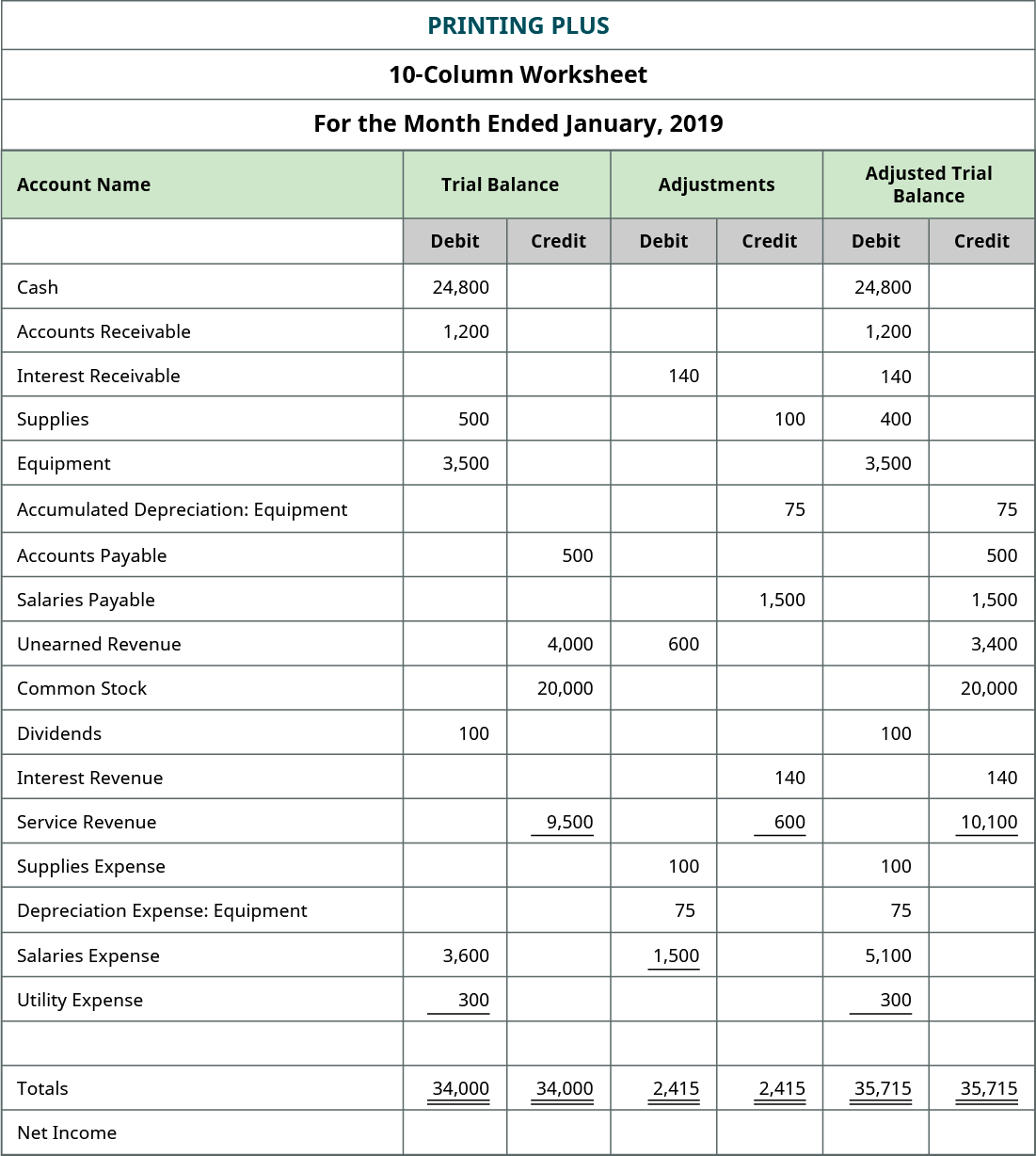
You will not see a similarity between the 10-column worksheetand the balance sheet, because the 10-column worksheet iscategorizing all accounts by the type of balance they have, debitor credit. To get the numbers in these columns, you take the number in thetrial balance column and add or subtract any number found in theadjustment column. There is no adjustment in the adjustment columns, so theCash balance from the unadjusted balance the better way to record prepayment amortisation in xero column is transferred overto the adjusted trial balance columns at $24,800. InterestReceivable did not exist in the trial balance information, so thebalance in the adjustment column of $140 is transferred over to theadjusted trial balance column. Presentation differences are most noticeable between the twoforms of GAAP in the Balance Sheet. Under US GAAP there is nospecific requirement on how accounts should be presented.
Adjusted Trial Balance Example
To simplify the procedure, we shall use the second method in our example. You could also take the unadjusted trial balance and simply add the adjustments to the accounts that have been changed. In many ways this is faster for smaller companies because very few accounts will need to be altered.
The list and the balances of the company’s accounts are presented after the adjusting journal entries are made at the year-end. Those balances are then reported on respective financial statements. Adjusted trial balance is not a part of financial statements; rather, it is a statement or source document for internal use. It is mostly helpful in situations where financial statements are manually prepared. If the organization is using some kind of accounting software, the bookkeeper or accountant just needs to pass the journal entries (including adjusting entries). The software automatically adjusts and updates the relevant ledger accounts and generates financial statements for the use of various stakeholders.
Adjusted Trial Balance
It shows a list of all accounts and their balances, either under the debit column or credit column. Both US-based companies and those headquartered in othercountries produce the same primary financial statements—IncomeStatement, Balance Sheet, and Statement of Cash Flows. One of the most well-known financial schemes is that involving the companies Enron Corporation and Arthur Andersen.
A trial balance only contains ending balances of your accounting accounts, while the general ledger has detailed transactions of the accounts. Notice the middle column lists the balance of the accounts with a debit balance, while the right column has balances for credits. Note that while a trial balance is helpful in the double-entry system as an initial check of account balances, it won’t catch every accounting error. The trial balance is a mathematical proof test to make sure that debits and credits are equal. Trial balances come in three key types, with each serving a purpose to help create accurate financial statements.
Once all ledger accounts and their balances are recorded, the debit and credit columns on the adjusted trial balance are totaled to see if the figures in each column match. Once all of the adjusting entries have been posted to the general ledger, we are ready to start working on preparing the adjusted trial balance. Preparing an adjusted trial balance is the sixth step in the accounting cycle. An adjusted trial balance is a list of all accounts in the general ledger, including adjusting entries, which have nonzero balances. This trial balance is an important step in the accounting process because it helps identify any computational errors throughout the first five steps in the cycle.
Let’s now take a look at the T-accounts and unadjusted trial balance for Printing Plus to see how the information is transferred from the T-accounts to the unadjusted trial balance. Debits and credits of a trial balance must tally to ensure that there are no mathematical errors. However, there still could be mistakes or errors in the accounting systems. A trial balance can be used to assess the financial position of a company between full annual audits. Take a couple of minutes and fill in the income statement and balance sheet columns. An income statement shows the organization’s financial performance for a given period of time.
