Degree of Operating Leverage Calculator
Alternatively, a company with a low DOL typically spends more money on fixed assets to increase its sales. Chartered accountant Michael Brown is the founder and CEO of Double Entry Bookkeeping. He has worked as an accountant and consultant for more than 25 years and has built financial models for all types of industries.
- If operating income is sensitive to changes in the pricing structure and sales, the firm is expected to generate a high DOL and vice versa.
- The company usually provides those values on the quarterly and yearly earnings calls.
- The degree of operating leverage (DOL) is a multiple that measures how much the operating income of a company will change in response to a change in sales.
- If sales and customer demand turned out lower than anticipated, a high DOL company could end up in financial ruin over the long run.
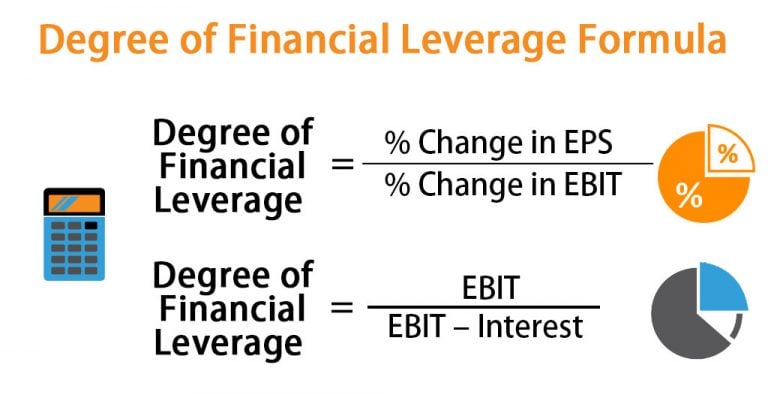
What Is the Difference Between DOL and Financial Leverage?
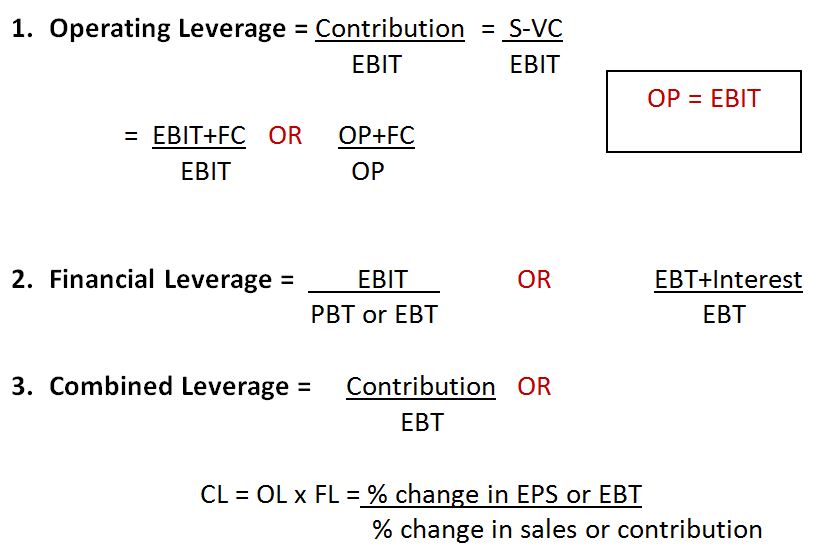
This means that a change of 2% is sales can generate a change greater of 2% in operating profits. Operating Leverage is a financial ratio that measures the lift or drag on earnings that are brought about by changes in volume, which impacts fixed costs. Many small businesses have this type of cost structure, and it 27 best freelance zapier developers for hire in february 2021 is defined as the change in earnings for a given change in sales. Conversely, Walmart retail stores have low fixed costs and large variable costs, especially for merchandise. Because Walmart sells a huge volume of items and pays upfront for each unit it sells, its cost of goods sold increases as sales increase.
How confident are you in your long term financial plan?
Next, if the case toggle is set to “Upside”, we can see that revenue is growing 10% each year and from Year 1 to Year 5, and the company’s operating margin expands from 40.0% to 55.8%. Just like the 1st example we had for a company with high DOL, we can see the benefits of DOL from the margin expansion of 15.8% throughout the forecast period. In the final section, we’ll go through an example projection of a company with a high fixed cost structure and calculate the DOL using the 1st formula from earlier. Despite the significant drop-off in the number of units sold (10mm to 5mm) and the coinciding decrease in revenue, the company likely had few levers to pull to limit the damage to its margins.
Do you own a business?
These two costs are conditional on past demand volume patterns (and future expectations). Furthermore, another important distinction lies in how the vast majority of a clothing retailer’s future costs are unrelated to the foundational expenditures the business was founded upon. One notable commonality among high DOL industries is that to get the business started, a large upfront payment (or initial investment) is required. Companies with higher leverage possess a greater risk of producing insufficient profits since the break-even point is positioned higher. For both the numerator and denominator, the “change”—i.e., the delta symbol—refers to the year-over-year change (YoY) and can be calculated by dividing the current year balance by the prior year balance and then subtracting by 1.
Great! The Financial Professional Will Get Back To You Soon.
With each dollar in sales earned beyond the break-even point, the company makes a profit, but Microsoft has high operating leverage. It is important to compare operating leverage between companies in the same industry, as some industries have higher fixed costs than others. On the other hand, if the case toggle is flipped to the “Downside” selection, revenue declines by 10% each year, and we can see just how impactful the fixed cost structure can be on a company’s margins. The DOL is calculated by dividing the contribution margin by the operating margin.
At the end of the day, the firm’s profit margin can expand with earnings increasing at a faster rate than sales revenues. If a company has high operating leverage, then it means that a large proportion of its overall cost structure is due to fixed costs. Such a company will enjoy huge changes in profits with a relatively smaller increase in sales. On the other hand, if a company has low operating leverage, then it means that variable costs contribute a large proportion of its overall cost structure. Such a company does not need to increase sales per se to cover its lower fixed costs, but it earns a smaller profit on each incremental sale.
However, if the company’s expected sales are 240 units, then the change from this level would have a DOL of 3.27 times. This example indicates that the company will have different DOL values at different levels of operations. This calculator simplifies the DOL calculation, facilitating a better understanding of financial leverage and operational efficiency for businesses, financial analysts, and students. This result indicates that for every 1% increase in sales, EBIT increases by 1.5%. Instead, the decisive factor of whether a company should pursue a high or low degree of operating leverage (DOL) structure comes down to the risk tolerance of the investor or operator.
However, if revenue declines, the leverage can end up being detrimental to the margins of the company because the company is restricted in its ability to implement potential cost-cutting measures. As said above, we can verify that a positive operating leverage ratio does not always mean that the company is growing. Actually, it can mean that the business is deteriorating or going through a bad economic cycle like the one from the 2nd quarter of 2020. In fact, there’s a relation between the two metrics, as the operating earnings can be increased by financing.
A business that generates sales with a high gross margin and low variable costs has high operating leverage. If a firm generates a high gross margin, it also generates a high DOL ratio and can make more money from incremental revenues. This happens because firms with high degree of operating leverage (DOL) do not increase costs proportionally to their sales. On the other hand, a high DOL incurs a higher forecasting risk because even a small forecasting error in sales may lead to large miscalculations of the cash flow projections. Therefore, poor managerial decisions can affect a firm’s operating level by leading to lower sales revenues. We can use the previous formula since the operating leverage ratio is related to the cost structure.
