Net Realizable Value NRV: Definition & Calculation
The total production and selling costs are the expenses required to facilitate the trade. When using NRV calculations for cost accounting, these expenses are the separable costs that can be identified or allocated to each good. Alternatively, this “expense” may be the anticipated write-off amount for receivables or expenses incurred to collect this debt.
Related AccountingTools Courses
A provision may be necessary if the write down to net realizable value is insufficient to absorb the expected loss – e.g. if inventory has not been purchased or fully produced. Unlike IAS 2, in our experience with the retail inventory method under US GAAP, markdowns are recorded as a direct reduction of the carrying amount of inventory and are permanent. There is no requirement to periodically adjust the retail inventory carrying amount to the amount determined under a cost formula. In other words, market was the price at which you could currently buy it from your suppliers.
Subscribe to the IFRS® Perspectives Newsletter
- Officials believe they have evidence that any eventual difference with the cash collected will be so small that the same decisions would have been made even if the exact outcome had been known at the time of reporting.
- There are still a hundred on hand, costs using FIFO, but the speakers are obsolete and management feels they can sell them with some slight modifications to each one that cost $20 each.
- By embracing technological advancements, businesses can stay ahead in an ever-evolving market and ensure their financial practices are robust and forward-thinking.
- A large company like Home Depot that has a consistent mark-up can reasonably estimate ending inventory.
- If a company has a contract to sell inventory for less than the direct cost to purchase or produce it, it has an onerous contract.
However, it can be complex to calculate, relies on estimates, and may lead to frequent adjustments due to market fluctuations. Under IAS 2, the cost of inventories measured using the retail method is reviewed regularly, in our view at least at each reporting date, to determine that it approximates cost in light of current conditions. The percentage of gross profit margin is revised, as necessary, what is a triple net nnn lease and whats included in it to reflect markdowns of the selling price of inventory. Because of various uncertainties, many of the figures reported in a set of financial statements represent estimations. Accounts receivable is shown at its net realizable value, the amount of cash expected to be collected. Losses from bad accounts are anticipated and removed based on historical trends and other relevant information.
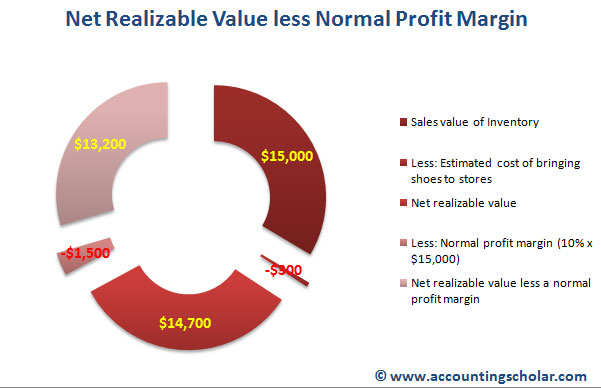
Calculating Net Realizable Value
Reversal, which is limited to the amount of the original write-down, is required for a subsequent increase in the value of inventory that was previously written down. The reversal of any write-down of inventories is recognized as a reduction in the cost of sales. Losses from a net realizable value analysis are not normally presented in a separate line item on a company’s financial statements. Instead, given their relatively small size (in most cases), they are buried within the cost of goods sold. However, the accountant could consider including them in the disclosures that accompany the financial statements.
In the transactions and events analyzed previously, uncertainty was rarely mentioned. The financial impact of signing a bank loan or the payment of a salary can be described to the penny except in unusual situations. Here, the normal reporting of accounts receivable introduces the problem of preparing statements where the ultimate outcome is literally unknown. The very nature of such uncertainty forces the accounting process to address such challenges in some logical fashion. Under IFRS, inventories may be measured and carried on the balance sheet at a lower cost and net realizable value.
Hence with conservative method NRV of Account Receivable for IBM is $9 Bn. However, it is important to know the steps to follow to make an accurate calculation besides knowing the formula. Listed below is a series of steps that one must consider for a reliable NRV analysis.
Understanding NRV will help you make more informed financial decisions and improve your business’s financial health. However, inventory i2 and the preparation cost to sell this inventory i2 remain the same at $70 and $30, respectively. The company states that as part of its calculation of inventory, the company wrote-down $592 million.
This is the gross amount of accounts receivable less any allowance for doubtful accounts reducing the total amount of A/R by the amount the company does not expect to receive. NRV for accounts receivable is a conservative method of reducing A/R to only the proceeds the company thinks they will get. Another advantage of NRV is its applicability, as the valuation method can often be used across a wide range of inventory items. Often, a company will assess a different NRV for each product line, then aggregate the totals to arrive at a company-wide valuation.
NRV provides a conservative estimate of an asset’s value, ensuring financial statements reflect realistic asset valuations. Net Realizable Value (NRV) is a vital concept in accounting that ensures assets, particularly inventory, are valued accurately in financial statements. By calculating NRV, businesses can prevent overvaluation of assets and provide a truthful representation of their financial health. This helps stakeholders make informed decisions and maintain trust in the company’s financial reporting. Inventory represents a significant part of the balance sheet for many companies. In accounting for inventory determining and capturing the costs to be recognized as an asset through the inventory lifecycle is key, because it affects a company’s KPIs such as gross profit margin.
If the loss is material, you may want to segregate it in a separate loss account, so that management can more easily spot these losses. Jami Gong is a Chartered Professional Account and Financial System Consultant. She holds a Masters Degree in Professional Accounting from the University of New South Wales. Her areas of expertise include accounting system and enterprise resource planning implementations, as well as accounting business process improvement and workflow design.
The general concept is to factor in the worst-case scenario of a firm’s financial future. Uncertain liabilities are to be recognized as soon as they are discovered. In contrast, revenues can only be recorded when they are assured of being received. Be aware the NRV can be used for external reporting (inventory and accounts receivable) purposes as well as internal reporting (cost accounting) purposes.
